Coronavirus (COVID-19) Updates
For the latest COVID-19 information and updates from Qatar Foundation, please visit our Statements page

Maria Onoufriou, a Senior Embryologist, highlights how egg freezing can ease women’s concerns about the ticking of their biological clock – and what they need to know about the process
Q. What is the difference between egg and embryo freezing?
Egg freezing - also known as egg/oocyte cryopreservation - is when eggs collected from a female patient are frozen and stored for future use.
Embryo freezing is when eggs are fertilized with the husband’s sperm, cultured to become embryos, and then frozen and stored for future use.


Egg freezing allows the preservation of woman’s reproductive potential that may be negatively affected by various factors, such as a medical condition or age
Q. How does egg freezing help women?
Egg freezing allows the preservation of woman’s reproductive potential that may be negatively affected by various factors, such as a medical condition or age.
The number of eggs in the ovaries decreases naturally and progressively during a woman’s lifespan. This is a natural process called atresia, and it starts early during the fetal stage: at 20 weeks of gestation, a female fetus will have 6-7 million eggs in the ovaries. This will decrease to 1-2 million at birth; 300,000-500,000 at puberty; 25,000 at the age of 37 and 1,000 or fewer at the age of 51, the average age of menopause.
What this means is that a woman’s fertility decreases gradually during her lifespan, but is significantly accelerated at the age of 32 and even more at the age of 37.
Egg freezing is offered to married women if there is no sperm available for fertilization at the time of egg collection, due to, for example, their husband being under medical treatment or traveling
Q. Are egg freezing and embryo freezing available at Sidra Medicine laboratories for all women?
Egg freezing is offered to married women if there is no sperm available for fertilization at the time of egg collection, due to, for example, their husband being under medical treatment or traveling.
It is also offered to single women for several medical reasons, such as cancer and severe benign gynecological conditions like advanced endometriosis). Cancer treatment regimens can be extremely harmful for fertility as they may cause severe damage to the ovaries and/or lead to early menopause.
Embryo freezing is only offered to married couples who wish to store embryos for medical or non-medical reasons.
Sidra Medicine laboratories currently offer egg freezing for various medical reasons.
Q. Is egg quality affected by age?
Yes, egg quality also declines with age. Increased maternal age strongly correlates with increased rates of DNA abnormalities in the oocytes. Therefore, older pregnant women are at higher risk of fetal DNA abnormalities and fetal loss (miscarriage).
Worldwide, it has been shown that more women delay childbearing in order to first achieve career goals, advance their education, and secure financial stability, as well as to find a suitable partner
Q. How can egg freezing help women who suffer from fertility anxiety due to aging? And what are the health and social benefits it can provide when it comes to family planning?
Worldwide, it has been shown that more women delay childbearing in order to first achieve career goals, advance their education, and secure financial stability, as well as to find a suitable partner. Elective Egg Freezing gives women the opportunity to extend their reproductive lifespan, help alleviate women’s concern about their biological clock, and allows them more time to reach their goals in life.
Q. What is the process of egg freezing? How long does it take - and is it painful?
The process consists of three stages:
-
Ovarian stimulation: Under medical supervision - which includes regular scans and blood tests - patients need to inject themselves daily with hormones to stimulate the ovaries and produce multiple eggs over a period of 7-10 days.
-
Egg Collection: Egg collection is performed 35-36 hours after the triggering of ovulation. While the patient is under sedation, the eggs are retrieved by the doctor, who uses a specialized needle and an ultrasound device for guidance. The actual egg collection procedure is painless, but some patients may experience discomfort and bloating after the procedure.
-
Egg Cryopreservation: Collected eggs are immediately transferred into the IVF lab, where the embryologist will assess their maturity. It is normal, and expected, that not all collected eggs will be mature and therefore suitable for freezing. Only mature eggs are frozen in a process called Vitrification. The patient is informed of the final number of frozen eggs 2-3 hours after egg collection.
Q. What does Vitrification mean?
Eggs are notoriously more difficult to cryopreserve than embryos, due to their high susceptibility to intracellular ice formation during freezing, which is detrimental to egg survival.
Vitrification is an ultrarapid freezing technique used in IVF labs that ensures the fast and maximized removal of water molecules from the egg cell, lowering the risk of ice formation when submerged in liquid nitrogen, the freezing agent. This technological breakthrough has considerably improved the reproductive success of egg freezing.
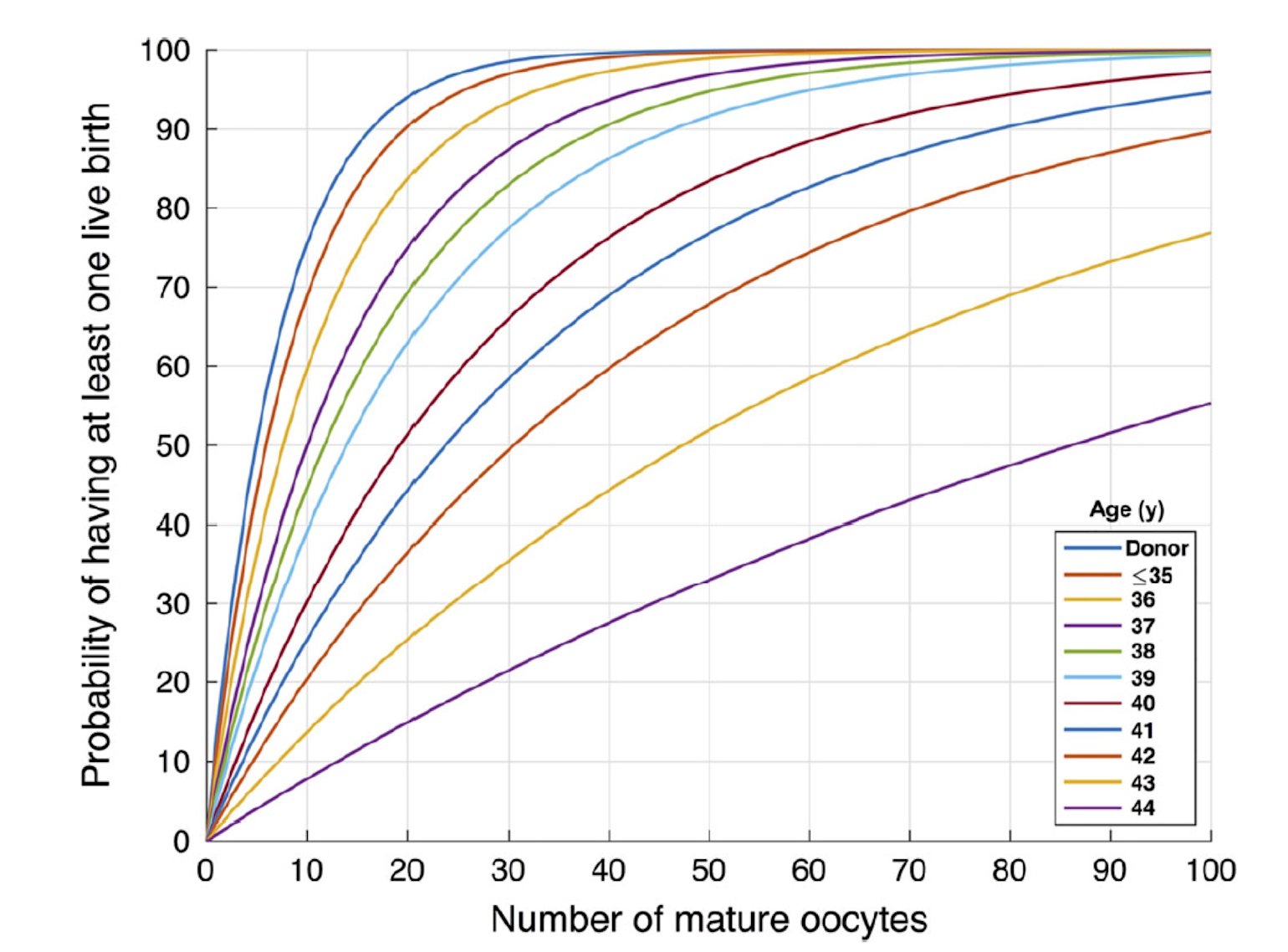
Q. What is the ideal number of eggs a woman needs to store for future use?
This is the most frequently asked question by women who are looking to freeze their eggs, and also the most challenging to answer, as it depends on several factors including maternal health and age, and future pregnancy goals. Unfortunately, no number of frozen eggs can guarantee a live birth.
In 2016, the below graph was developed as a counseling tool, to predict the likelihood of one live birth based on age at egg collection and number of eggs frozen. This evidence-based model is now widely used by doctors to provide reasonable expectations to patients, as well as to help them realize that no matter how many oocytes are frozen, the likelihood of a live birth can never reach 100 percent. It also helps patients decide how many cycles of egg freezing they should undergo, while demonstrating that there is a point beyond which additional cycles may not be beneficial.
Q. What happens when a woman wants to use her stored eggs?
When a woman is ready for a family, her frozen eggs are warmed and used to create embryos. Warmed eggs are fertilized by injecting a single sperm in the center of the egg using a micro-needle, a process called Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI). Once the eggs are fertilized – and are now called embryos - they are cultured for 3-5 days in order to assess their quality. Good quality embryos are then transferred into the uterus of the female patient using a thin catheter – the embryo transfer procedure.
As long as the clinic ensures uninterrupted optimum storage conditions, frozen eggs can be stored as long as the woman wishes. Pregnancies have been reported after using eggs frozen for 10 years, which is reassuring considering that egg freezing is a relatively new field of IVF.
Q. What are the success rates?
Several studies in the past few years have demonstrated improved survival, fertilization, and pregnancy rates with the use of vitrification versus the old ‘slow freezing’ method. Additionally, a recent meta-analysis found that the rates of fertilization, high quality embryos and ongoing pregnancy did not differ between vitrified-warmed and fresh eggs used for ICSI, the procedure where a single sperm is injected directly into the cytoplasm of the egg.
Q. Are any tests necessary prior to egg freezing?
Yes, there is a specific hormonal blood test that a woman must do before freezing her eggs, which can provide a reliable indication of her ovarian reserve and the number expected to be obtained per treatment cycle. This test can help the doctor to tailor the ovarian stimulation protocol accordingly – the type of medication and dosage - in order to maximize the number of eggs obtained from a treatment.
In addition to the blood test, fertility doctors may request ultrasound examination of the uterus and ovaries, during which they can perform an antral follicle count - visually counting the number of egg follicles that appear on both ovaries. A high count indicates a good egg yield, often meaning that a good number of eggs can be retrieved during the treatment cycle.
For more detailed information, I recommend women book a consultation appointment with a fertility specialist.
Q. What are the long-term obstetric and perinatal outcomes associated with oocyte cryopreservation? Is egg freezing safe for women and their babies in the future?
Recent studies have shown that the mean birthweight and incidence of congenital abnormalities were similar between infants born from natural pregnancies and infants born after oocyte vitrification-warming-ICSI. It was therefore concluded that egg freezing, followed by warming and ICSI, does not negatively affect obstetric and perinatal outcomes. However, despite the scientific reassurances regarding the efficiency and safety of the procedure, it is important to remember that as this is a relatively new medical achievement, no long-term follow-up studies of these children have yet been conducted.

